Creation of resources listing all the tools and their metadata relevant to your community
| Author(s) |
|
| Reviewers |
|
OverviewQuestions:
Objectives:
Is it possible to have an overview of all Galaxy tools for a specific scientific domain?
How can I create resources listing all the tools relevant to a Galaxy community or domain?
Create community reviewed resources for Galaxy tools within a specific scientific domain
Time estimation: 1 hourLevel: Introductory IntroductorySupporting Materials:
Published: Mar 13, 2024Last modification: Oct 28, 2025License: Tutorial Content is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The GTN Framework is licensed under MITpurl PURL: https://gxy.io/GTN:T00475version Revision: 5
Galaxy offers thousands of tools. They are developed across various GitHub repositories. Furthermore, Galaxy also embraces granular implementation of software tools as sub-modules. In practice, this means that tool suites are separated into Galaxy tools, also known as wrappers, that capture their component operations. Some key examples of suites include Mothur and OpenMS, which translate to tens and even hundreds of Galaxy tools.
While granularity supports the composability of tools into rich domain-specific workflows, this decentralized development and sub-module architecture makes it difficult for Galaxy users to find and reuse tools. It may also result in Galaxy tool developers duplicating efforts by simultaneously wrapping the same software. This is further complicated by a lack of tool metadata, which prevents filtering for all tools in a specific research community or domain, and makes it all but impossible to employ advanced filtering with ontology terms and operations like EDAM ontology.
The final challenge is also an opportunity: the global nature of Galaxy means that it is a big community. Solving the visibility of tools across this ecosystem and the potential benefits are far-reaching for global collaboration on tool and workflow development.
To provide the research community with a comprehensive list of available Galaxy tools, Galaxy Codex was developed to collect Galaxy wrappers from a list of Git repositories and automatically extract their metadata (including Conda version, bio.tools identifiers, and EDAM annotations). The workflow also queries the availability of the tools and usage statistics from the three main Galaxy servers (usegalaxy.*).
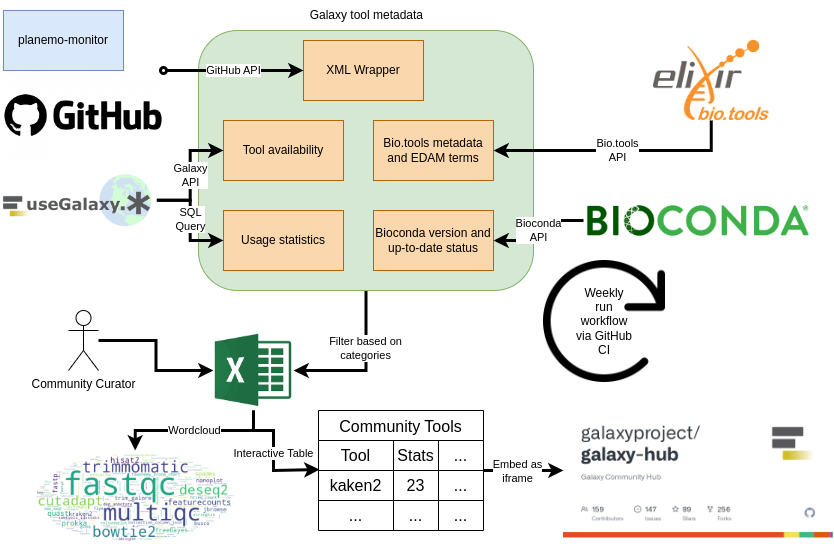 Open image in new tab
Open image in new tabThe pipeline creates a table with all tools and their metadata. This table can be filtered to only include tools that are relevant to a specific research community. Here is an example for the microbial related tools:
The generated community-specific table can be used as is (e.g. downloadable tsv file) and/or embedded (e.g. into a Galaxy Hub page or Galaxy subdomain). This table allows further filtering and searching for fine-grained tool selection.
The pipeline is fully automated and executes on a weekly basis. Any research community can apply the pipeline to create a table specific to their community.
The aim of this tutorial is to create such table for a community.
AgendaIn this tutorial, we will cover:
Add your community to the Galaxy CoDex
You first need to check if your Community is in the Galaxy CoDex, a central resource for Galaxy communities. If the community is already there, you can move to the next step of this tutorial.
If you community is not already included, follow these steps :
Hands On: Add your community to the Galaxy CoDexYou need to create a new folder in the data/community folder within Galaxy CoDex code source.
- If not already done, fork the Galaxy Codex repository
- Go to the
communitiesfolder- Click on Add file in the drop-down menu at the top
- Select Create a new file
- Fill in the
Name of your filefield with: name of your community +/metadata/categoriesThis will create a folder for your community, a new folder for your community called metadata and a file called categories.- Click on Commit changes
- Fill in the commit message with something like
Add X community- Click on
Create a new branch for this commit and start a pull request- Create the pull request by following the instructions
Pull list of tools relevant to your community from the Galaxy ToolShed
To add tools in your community tool table, you will need to indicate a list of tags relevant to your community, and tools associated with this tag will be automatically pulled from the Galaxy ToolShed on a weekly basis. Only tools in the selected ToolShed categories will be added to the filtered table. As a result, it is recommended to include broad categories. You will then be able to remove tools that are not relevant to your community or deprecated.
Hands On: Select the ToolShed categories
- Go to the Galaxy ToolShed
- On the main page, pick the most obvious categories that represent tools used by your community and note the names of these categories
- Search on the Galaxy ToolShed for some of the popular tools in your community
- Open the tool entries on the ToolShed, and note their categories
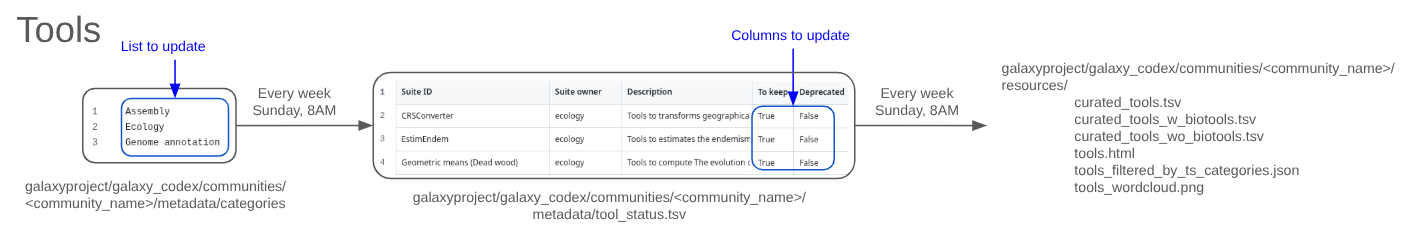
Add the list relevant tags for your community in the categories file
Hands On: Add the ToolShed catgories to the categories file
- Open or create the file named
categoriesin your community metadata folder (communities/<your community>/metadata/categories)Add the name of the categories relevant to your community in the
categoriesfile you started above, with 1 ToolShed category per row. For example, see a list of valid ToolShed categories.For example:
Assembly Metagenomics
Once you have a list of the ToolShed categories that you wish to keep, you can submit this to Galaxy CoDex.
Hands On: Submit the new list of categories to Galaxy CoDex
- Click on Commit changes at the top
- Fill in the commit message with something like
Add tools categories for my community- Click on
Create a new branch for this commit and start a pull request- Create the pull request by following the instructions
The Pull Request will be reviewed. Make sure to respond to any feedback.
On the Sunday following the merge of the previous pull request, two files will be generated :
- A JSON file with all tool suites and a short description will be created in
communities/<your community>/resources/tools_filtered_by_ts_categories.json. - A table with all tool suites and a short description will be created in
communities/<your community>/metadata/tool_status.tsv.
Review the generated table to curate tools
The generated table will contain all the tools associated with the ToolShed categories that you selected. However, not all of these tools might be interesting for your community.
Galaxy Codex allows for an additional optional filter for tools, that can be defined by the community curator (maybe that is you!).
The additional filter must be stored in the file called tools_status.tsv located in communities/<your community>/metadata. The file must include at least 3 columns (with a header):
Suite IDTo keepindicating whether the tool should be included in the final table (TRUE/FALSE).Deprecatedindicating whether the tool is deprecated (TRUE/FALSE).
Example of the tools_status.tsv file:
Suite ID To keep Deprecated
abacas TRUE FALSE
abricate TRUE FALSE
abritamr TRUE FALSE
To generate this file, we recommend you to use the generated file tools_status.tsv and to simply update the last two columns.
Hands On: Review tools in your community table
- Download the
tools.tsvfile.- Open
tools.tsvwith a Spreadsheet Software.Review each line corresponding to a tool.
You can also just review some tools.
- Add
TRUEto theTo keepcolumn if the tool should be kept, andFALSEif not.- Add
TRUEorFALSEalso to theDeprecatedcolumn.- Export the new table as TSV.
- Submit the TSV as
tools_status.tsvin your community folder.- Wait for the Pull Request to be merged
On the Sunday following the merge of the previous pull request, a curated_tools.tsv file will be generated in communities/<your community>/resources/ folder reflecting the Galaxy tool landscape for your community. You or other community members can review tools in your community from this page to make step-by-step changes or updates to the tools_status.tsv file as needed.
We recommend collaborative work be done with a cloud-based system such as a Google Sheets page.
Here is an overview of the files (the top three files in the table are the most important):
| Filename | Location | Generation | Function | Format | Example (microgalaxy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| categories | communities/ |
Manual | Name of the categories relevant to your community, with 1 ToolShed category per row | NA | Example |
| tool_status.tsv | communities/ |
Automatic (to update manually) | Table with all tool suites and a short description | TSV | Example |
| curated_tools.tsv | communities/ |
Automatic | Curated table with all tool suites and a short description | TSV | Example |
| curated_tools_w_biotools.tsv | communities/ |
Automatic | Curated table with all tool suites that have a biotools ID | TSV | Example |
| curated_tools_wo_biotools.tsv | communities/ |
Automatic | Curated table with all tool suites without a biotools ID (You can add them on BioTools or link them!!) | TSV | Example |
| tools.html | communities/ |
Automatic | A list of the tools in html format to include in a website | HTML | Example |
| tools_wordcloud.png | communities/ |
Automatic | A wordcloud with the tools used the tool suites | PNG | Example |
 Open image in new tab
Open image in new tabEmbed the interactive table in your community page on the Hub
The interactive table you have created can be embedded in your community page on the Hub, e.g. microGalaxy.
Hands On: Embed your table as an iframe
- If not already done, fork the repository Galaxy Hub
- Open or create your community page:
content/community/sig/<your community>/index.mdAdd an iframe to embed the interactive table
<iframe id="inlineFrameExample" title="Microbial related tools" width="100%" height="600" frameBorder="0" src="https://galaxyproject.github.io/galaxy_codex/communities/<your_community>/resources/"> </iframe>- Replace
<your_community>by the name of your community insrc- Submit the changes
- Wait for the Pull Request to be merged
Conclusion
You now have curated resources listing Galaxy tools available for your community, and this table can be embedded in a community page.